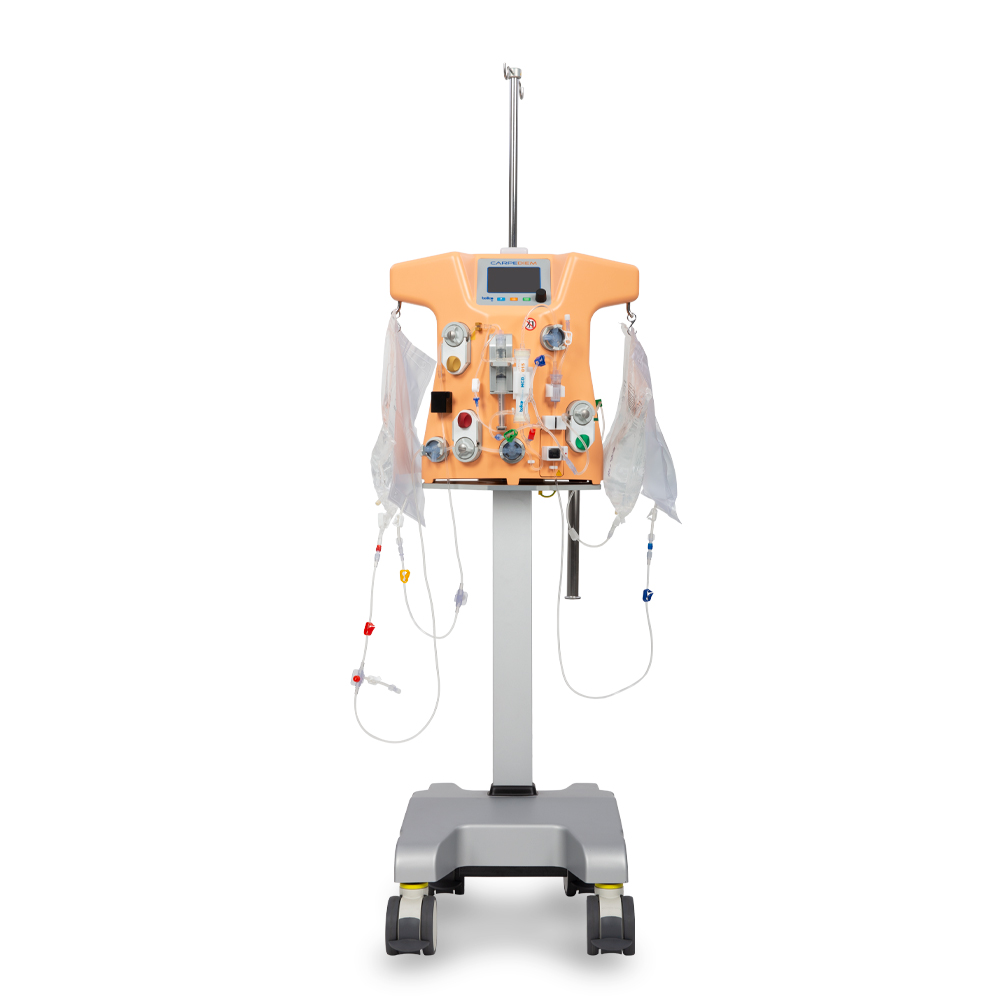

Carpediem™ cardio renal pediatric dialysis emergency machine
Provides continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) for acute kidney injury and fluid overloaded pediatric patients weighing 2.5 to 10 kgs.
Innovations in pediatric CRRT
For the first time, infants with acute kidney injury (AKI) and fluid overload (FO) can be treated with a dialysis system designed specifically for them.1
A miniaturized, high-precision platform1,2
The first of its kind, the Carpediem™ system offers a dedicated extracorporeal CRRT to low weight patients and responds to the needs of the most fragile patient.
- CVVH, CVVHD, and SCUF modalities
- Low priming volume and pump flow
- High-precision scales
- Continuous or bolus heparin pump delivery
When size and scale matter.
Neonatal acute kidney injury (AKI) and fluid overload are under-recognized conditions which often lead to morbidity and mortality.3
97%
neonate survival rate upon discontinuation of treatment.4,†
Tailored performance. Precise control.
- Closely monitor fluid balance:
+/- 1 g high-precision scales2 - Enable use of small catheter sizes5
- Reduce blood cell and vessel damage while providing necessary and adequate diffusive clearances: 2–50 mL/min low blood flow rates1,2,6
A renewed focus on what is most important.
For the first time, there is no need to adapt adult machines and weigh the complexities that have traditionally plagued pCRRT treatments.7
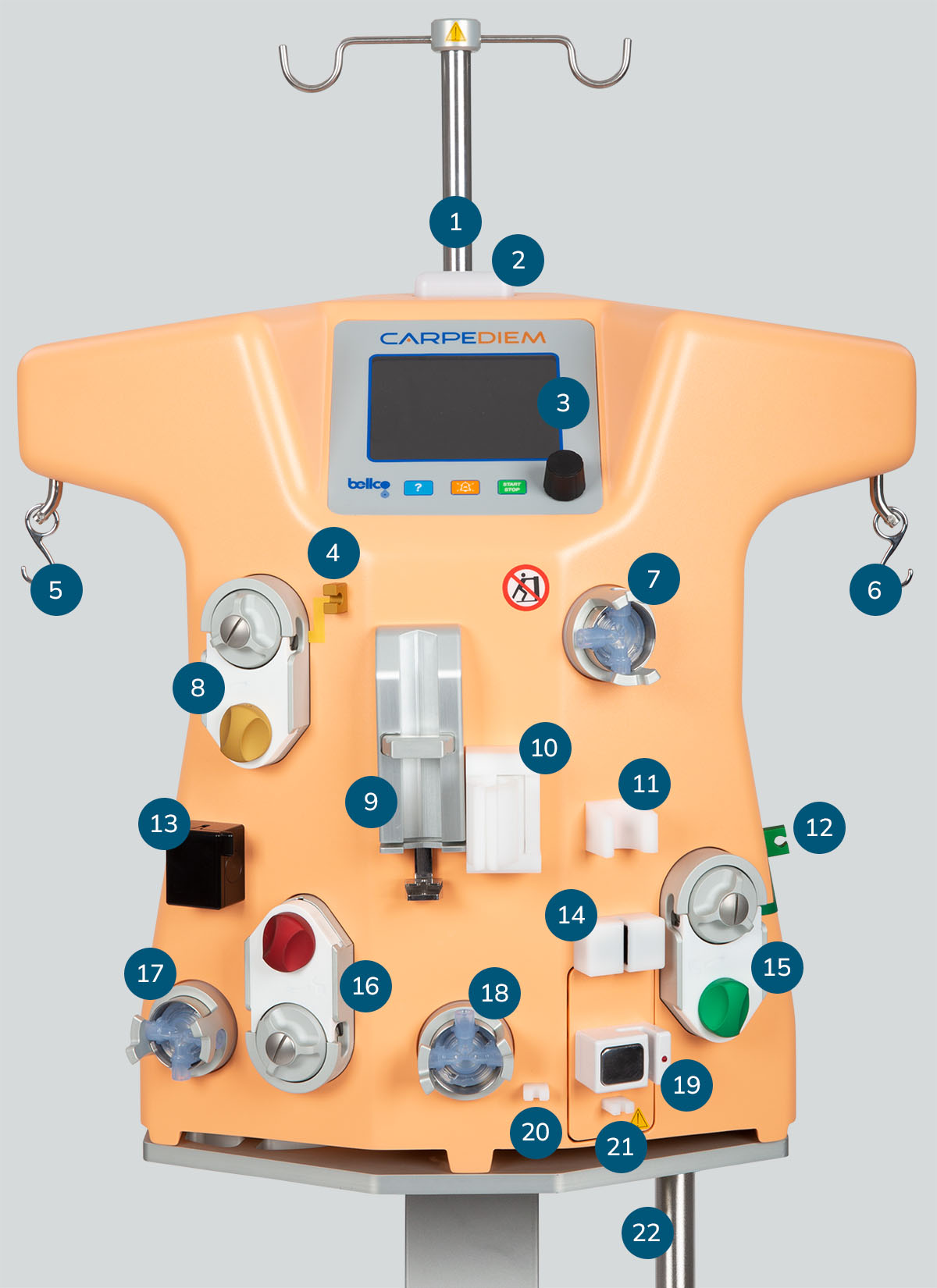
Carpediem™ system details
- IV pole holder
- Warning light
- Control panel
- Clip for effluent (EFF) pump segment
- Effluent (EFF) scale
- Infusion/dialysis (INF/DIA) scale
- Venous pressure transducer (dome)
- Effluent (EFF) pump
- Heparin pump
- Filter holder
- Venous drip chamber holder
- Clip for the infusion/dialysis (INF/DIA) pump segment
- Blood leakage detector (BLD)
- Air sensor
- Infusion/dialysis (INF/DIA) pump
- Blood pump
- Arterial pressure transducer (Dome)
- Pre-filter pressure transducer (Dome)
- Venous electroclamp
- Clip for infusion/dialysis (INF/DIA) line if a warmer is used
- Clip for venous line
- Warmer holder
Customer support
For ordering support and general enquiries:
Phone: 800.962.9888
Fax: 800.637.9775
Reimbursement and procedure coding
Explore guidelines to help your staff optimize the process of procedural CPT and HCPCS code selection.
Equipment services
For maintenance plan and technical support:
Hours: 8 a.m. – 6 p.m. Central Time
Phone: 800.255.6774
Select option 5, then option 1
Clinical support and tailored training
24/7 guidance from Carpediem™ pCRRT experts
Carpediem™ system support includes:
- Tailored training specific to each individual care setting
- On-site system installation
- On-demand, 24-hour emergency access to registered nurses experienced in pCRRT and the Carpediem™ system
†50% Carpediem™ system patients survived to ICU discharge. Mortality after pCRRT discontinuation due to critical illness with underlying pathologies – many not amenable to treatment.4
- Ronco C, Garzotto F, Ricci Z. CA.R.PE.DI.E.M. (Cardio-Renal Pediatric Dialysis Emergency Machine): evolution of continuous renal replacement therapies in infants. A personal journey. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27(8):1203–1211.
- Carpediem™ dialysis system [Operator’s Manual]. Minneapolis, MN: Medtronic; 2022.
- Nada A, Bonachea EM, Askenazi DJ. Acute kidney injury in the fetus and neonate. Sem Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;22(2):90-97.
- Goldstein SL, Vidal E, Ricci Z, et al. Survival of infants treated with CKRT: comparing adapted adult platforms with the Carpediem™. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022;37(3):667-675.†
- Vidal E, Cocchi E, Paglialonga F, et al. Continuous veno-venous hemodialysis using the Cardio-Renal Pediatric Dialysis Emergency Machine™: first clinical experiences. Blood Purif. 2018;31:1–7.
- Garzotto, F, Zaccaria M, et al. Choice of Catheter size for infants in Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: Bigger Is Not Always Better. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 2019;20(3): 170-179.
- Ronco C, Garzotto F, Brendolan A, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy in neonates and small infants: development and first-in-human use of a miniaturised machine (CARPEDIEM). Lancet. 2014;383:1807–1813.
